Digital Insights
Net Neutrality: Awareness of the Existence of Equality in the Internet in Southeast Asia
Published
6 years agoon
By
SEADS TEAM
When we say the internet, what comes to mind are three basic principles: openness, fairness, and freedom. It is through the internet that we are able to fully express ourselves in an equal playing field.
According to We Are Social, the overall count of internet users around the world up to date is 4.39 billion. In this huge number of users, you wouldn’t think there won’t be any problems in accessing your website, right? Nope.

Some Internet Service Providers or ISPs have prioritized other businesses or websites in favor of the other. An example of this is Netflix. Comcast, an ISP cable company in the US had slowed down users’ access to Netflix to prioritize its competitor, Hulu.
By striking a negotiation, Netflix agreed to pay Comcast to make sure that their services don’t have any hindrances moving forward. But, was striking a deal and making a payment in this situation necessary? I think not. That’s why net neutrality was established.
What is Net Neutrality?

Net neutrality makes sure everyone has an equal playing field on the internet. This promotes anti-prioritization of ISPs to specific businesses within the range of their service to users.
The term has been coined by Tim Wu back in 2003. It has been presented and used in the US as a way to provide freedom in accessing any website available.
Pros and Cons of Net Neutrality
Like most things, net neutrality has two sides.
Pros of Net Neutrality

Freedom of Speech and Anti-Discriminatory Practices
Coming from the name itself, it promotes neutrality and equality. Any user can roam any website they please.
Aside from that, it also promotes freedom of speech. As a result of having access to any website, you are free to express yourself in your own blog or offer services from your business website. There is no censorship provided, as long as it is legal.
Innovation Promotion
Being granted access to any website promotes innovation as long as you have all access anywhere. In this way, existing and startup companies are able to grow and innovate their products and services.
Monitored Illegal Activities
Net neutrality promotes innovation and accommodation. It does not mean that it does not include criminal activities. ISPs will regulate as a common carrier, to prevent any illegal activities or illegal file sharing.
Cons of Net Neutrality

Non Compensation of Data Consumption and Unregulated Internet Access
As the internet grows, we are present in this day and age where we can video-call anyone via Skype or live stream. As a result, it utilizes higher volumes of bandwidth without charging the use according to the data consumed, therefore no compensation whatsoever.
As net neutrality makes the internet a fully accessible platform for anything and anyone, there is a risk of unregulated internet access. Any content can be accessed by anyone, creating risks of posting and uncovering insensitive and obscene content.
Innovation Stifled
Technology usually involves innovation. Yes, as mentioned above, net neutrality promotes innovation. However, since this concept also promotes having fair access and equal playing field to all websites and businesses, it means bringing bandwidth-heavy services.
It is possible that due to this, it will provide less opportunity for ISPs to do any innovation or upgrades of the services offered to us.
Effects of Net Neutrality
Net neutrality affects everything on the internet, businesses and consumers alike.
Effect to Businesses
Providing Fair Competition
Net neutrality safeguards fair competition. Startup businesses are given equal opportunities to be discovered and to grow on the internet. Net neutrality becomes a middleman, preventing anti-prioritization from ISPs.
No Room for Upgrades
A considered disadvantage of having net neutrality is having no room for upgrades. As users will have the power to access anything all at the same speed, it equals to higher-bandwidth.
You may say that your provider can promise to provide high internet speed, but there is a higher possibility your ISP would be unable to provide it for everyone every time, as there will be no time to make any adjustments.
Effect to Consumers
Providing Fair Access for Everyone
Net neutrality also plays the role of safeguarding consumers online. Having fair access to any websites equals saving money in your pockets. It protects us in paying extra compensation to ISPs just to access specific sites.
Abuse of Privilege
Too much exposure in the digital space may be a disadvantage in terms of net neutrality. If you think about it, it is possible for people to abuse the privilege that net neutrality provides.
Internet Freedom in Southeast Asia
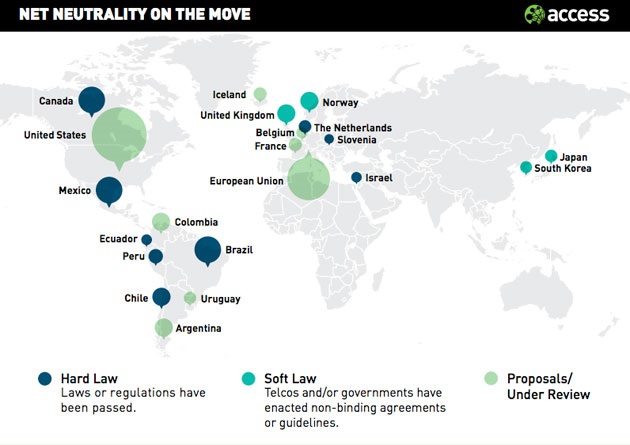
Source: MarketWatch
The internet is an important platform in this day and age. It is where we exercise our privilege of digital rights, freedom of information, internet access right, internet censorship freedom, and net neutrality. That’s we call internet freedom. Now the question here is this: is internet freedom being practiced in all of Southeast Asia?
Cambodia
In Cambodia, there are internet freedom restrictions. Due to civil society repression, access to the internet declined. A number of individuals were arrested due to online activities which resulted in heightened self-censorship.
The restriction grew in recent years. It came to the point that they had shut down and blocked the website of Cambodia Daily, a renowned English-language newspaper that discovered a number of corruption scandals and human rights abuses in Cambodia.
According to the Freedom House report, having authoritarian Hu Sen in power, its restricted internet freedom, especially last 2018.
Philippines
Internet freedom in the Philippines declined in 2018 due to an increasing number of cases filed against journalists regarding critical reporting and increasing surveillance concerns.
Rappler, an online news network, was ordered shut down by President Duterte due to alleged “weaponizing” of social media, reporting criticisms against the present administration.
Malaysia
The decline in internet freedom in Malaysia happened in 2018 due to the Fake News Act 2018. This law condemns anyone spreading fake news in any way, in any platform.
Politicians, websites and political parties were also targeted by technical attacks during the general elections in 2018. On a positive note, there is less violence and intimidation against online journalists and internet users.
Singapore
In Singapore, internet freedom is stable. Governments established active promotion of digital technologies while restricting their use for political dissent and the expression that could cause friction between ethnic or religious communities
In May 2018, the Public Order and Safety Act was established. This only effectively restricts online media and freedom of speech during “serious incidents”.
Thailand
Even though there is no internet freedom in Thailand for the fifth year in a row, there is still a slight improvement. There has been increased access through the web and less violence directed against online journalists and information and communication technology users.
Vietnam
Vietnam has a characterized draconian repression on activists and online expression, resulting in high restriction of internet freedom.
Hundreds of Facebook accounts and YouTube videos are removed due to online content manipulation. It was claimed to be “spreading reactionary, anti-party, anti-state information, defaming Vietnamese leaders and the state”. As a result, the military unit called Force 47 was established.
Alongside this, the imprisonment of 25 bloggers, including blogger Mother Mushroom and Hoang Duc Binh had set the second repression experienced against an online speech by Vietnam.
In June 2018, a new cybersecurity law was passed stating that it will be implementing restrictions on freedom of expression online, prohibitions on the use of the internet to the state, distortion of Vietnam’s revolutionary history and achievements, spreading false information, and harmful socioeconomic activities.
Also, social media companies need to comply within the day once a content removal request was made by authorities.
Myanmar
The diversity of content available in Myanmar decreased as government and military continued to further entrench the state narrative about the Rohingya crisis. Intimidation, violence increased for online activists and journalists, even going as far as attempted murder.
As a result, Facebook did its best in removing content and account relating to the crisis. The platform’s blocking and filtering process have been non-transparent with a limited avenue for appeal.
Alongside this, the government established the “Social Media Monitoring Team”, claimed to target pro-Rohingya activists, international civil society organizations, and foreign media.
Indonesia
From blockage under the ruse of fake news, terrorism, and pornography, social media platforms suffered. In the meantime, LGBTI content was continually targeted for censorship.
A crawler system driven by AI tools called Cyber Drone 9 was launched by the government to detect violations and flag content for blocking.
In fighting against terrorism, amendments to the 2003 Eradication of Criminal Acts of Terrorism Law (CT Law) was adopted in May 2018. It sweeps surveillance powers.
India
In August 2017, the number of local internet shutdowns increased, new rules regulating connectivity restrictions are announced. At the same time, privacy is also ruled as a fundamental right by the Supreme Court.
Amidst this, India formed a committee that will develop a data protection framework called the Srikrishna committee. In July 2018, their report was published, which raised controversies from the civil society and tech companies, including the ability to facilitate government surveillance through data localization requirement.
As for net neutrality, the rules were proposed back in November 2017 by the Telecom Regulatory Authority, which was later passed after the coverage period in July 2018
Alternatives of Net Neutrality in Southeast Asia

Most countries within Southeast Asia do not have internet freedom, let alone net neutrality. However, there are some alternatives that have similarity with the concept.
Magna Carta for Philippine Internet Freedom
The Magna Carta for Philippine Internet Freedom is a crowdsourced document filed as a Senate Bill by Miriam Defensor-Santiago and filed as a House Bill by Kimi Cojuangco.
It aims to protect the rights and freedom of Filipinos in cyberspace, which is similar to net neutrality. This will effectively repeal Republic act 10175 Cybercrime Prevention Act.
Malaysia’s Communication and Multimedia Act 1998
The Communication and Multimedia Act 1998 is the act of creating a new system of licenses and clarify the roles and responsibilities and ensures that information, network, and service is safe, reliable and affordable in all of Malaysia.
The internet is one of the things that everyone has in common. All of us use it in our daily lives. Having no freedom to access or to use it at all can be quite difficult. However, you also need to consider the consequences in terms of using that freedom specifically.
So, what now?
Net neutrality is like a double-edged sword. There are factors that can help you boost your visibility on the internet. We are lucky to have this level of user-friendly technology.
Net neutrality in Southeast Asia is not discussed as it is in the US. As the repression of respective governments mostly overpowers citizens, both businesses and consumers can and should work hand in hand in spreading awareness of net neutrality and making sure everyone benefits in using the internet.












