Future of Work
What Does a Digital-First World Look Like?
Published
2 years agoon
By
SEADS TEAM
The myriad digital tools and applications we use today are just a sneak peek of what the future holds. It is constantly evolving, and many developments stay permanently in the lives of every individual and demographic.
World economies thrive with the help of technology and information necessary to innovate and create.
The United States and countries in Scandinavia became the standard of a digital-first nation. But what are the leaders of developing nations doing for a digital-first world?
What does a digital-first world look like?

Similar to the traditional economy, the digital-first world runs on capital. The major difference is the digitalization of this process.
We are slowly transforming into a digitalized world with ease of access to finance through online applications, easier eB2B transactions, and more.
Driven by three factors: internet connectivity, data, and electronics, the digital-first world is a community not limited by geographical locations or boundaries.
And technology moves fast. As portrayed in the movie Transporter Refueled, they highlighted how as soon as you think technology can’t come up with anything more, it comes up with something else.
The changes in digital involve every sector of the economy, from the producers to the consumers. Here are the pillars of a digital-first world.
Pillars of a digital-first world
Businesses: 95% of businesses implement a digital-first strategy to support digital revenue streams. This is to cater to new consumers who find digital transactions easier than traditional ones.
By 2027, industry experts believe that 47% of every business revenue will come from digital products and services. This includes digital self-services and digital interaction with sales.
Businesses leverage the internet to access data and centralize their competitors’ and consumers’ records. Reporting and analytics, insight tools, and data management tools are some of what they use today, and soon there will be more.
Government: Digital accelerates a country’s economic growth. In the past years, Southeast Asian leaders have implemented e-governance bills to build a digital economy. The Philippines even refiled their E-government Act of 2022 to quicken their digital transformation. These bills and programs can improve the citizen’s media and information literacy, digital literacy, and increase internet connectivity.
The inconvenience brought by outdated government processes hinders citizens and businesses from success. In a fast-paced digital world, improvements in government technology are necessary.
Consumers: The major driving force for the digital economy is the consumers. And by 2024, 80% of the world’s population will be online. When consumers do not participate in the use of technology in their daily lives, the digital shift slows down.
This is evident in cases of foreigners who live in cashless countries and visit countries behind in digitalization. When the ease of transactions is normalized, the inconveniences of traditional transactions are noticeable.
The advantages of a digital-first world
For businesses: Digital improves business efficiency.
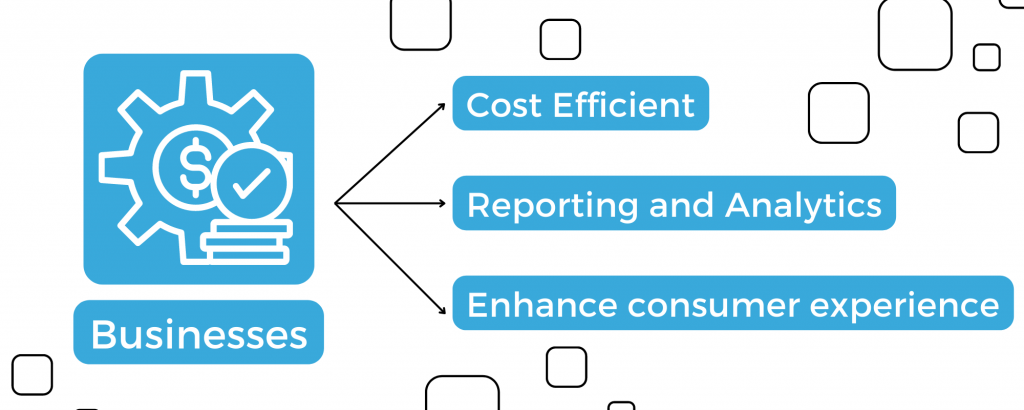
- Cost efficient: Digital limits human error that commonly costs a business. Digital knowledge management reduces messy manuals and overhead costs.
- Reporting and analytics: Data-based insights can convert into actionable, revenue-generating insights. It can improve corporate decision-making with analyzed, translated, and processed data.
- Enhance customer experience: Personalized services enhance the customer experience. Digitized and automatic processes increase customer satisfaction with frictionless Ai, automation, and self-service tools.
For society: Digital improves industries like travel, shopping, entertainment, working, communications, and more.
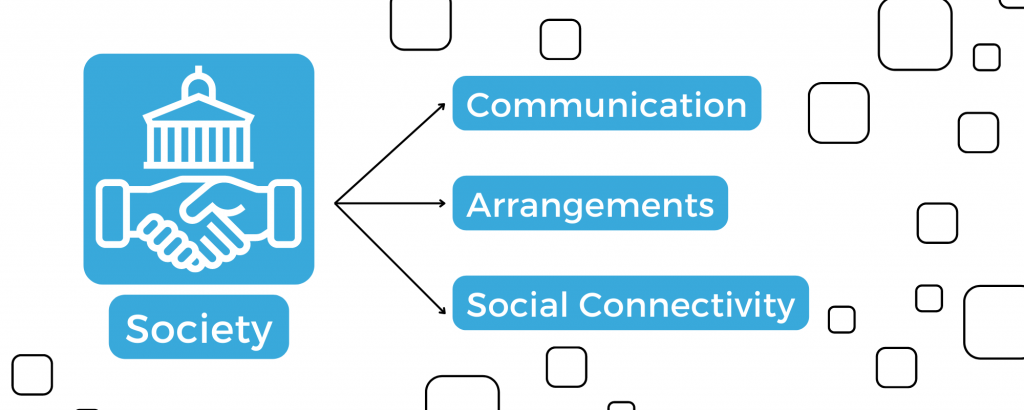
- Communication: With increasing internet speed, communication became even faster. The web allows sharing any size of data, streaming live in audio and video of any quality, and more.
- Arrangements: Working from home, online education, online appointments, telehealth; the arrangements dictate convenience. GPS and mapping make traveling frictionless with less worry of being lost.
- Social Connectivity: Staying in touch with friends from anywhere in the world is just the tip of the iceberg. Socializing in a digital-first world is more than words, audio, and video, but any multimedia exchange.
For consumers: Over 4.4 billion monthly active users will join the internet by 2025. Consumer electronics drove expenditure during the previous two decades and digital services like online education, peer-to-peer financing, and subscription-based services will drive spending over the following two years.
In a digital-first world, consumers will have new priorities, including:
- Scalability: How will businesses cost-effectively scale their digital operations?
- Trustworthiness: How will businesses effectively establish themselves as a reputable organization?
- Safety: How does a business keep customer information secure and safe?
- Digital practices: How will businesses innovate their digital experience and services?
- Sustainability: How will businesses practice digital experience without harming the environment, society, and government?
Technology building blocks of a digital world
Accelerated by the pandemic, more than half of the world uses digital. And the United Nations see the opportunity to use the momentum to create a sustainable digital-first world.
The building blocks of a digitalized world influence industries, businesses, and organizations to leverage digital in the way they create, innovate, and deliver their operations while empowering employees, consumers, and people.
Digital Strategy: Backed up by value, data, and analytics, a digital strategy is a goal towards digitalization communicated to businesses, governments, and consumers.
Digital Literacy: The knowledge and practice of the citizens in using, navigating, and personalizing digital.
Operational Process Automation: Simplification and elimination of non-essential tasks for every process which involves the pillars of a digital nation.
Change and Speed: Digital innovation is constantly changing. Citizens should adapt to every change.
Identifying Disruptors: Predicting the disruptions for digital transformation before it happens.
SEA’s Digital-First World: Singapore
According to Bain & Company, there are six major economic drivers in Southeast Asia which include: Singapore, Philippines, Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, and Vietnam. The excluded countries from SEA include Myanmar which is currently battling a political war, Timor Leste, and Laos.
The report also includes the achieved milestones of the digital efforts of the Southeast Asian Nations including the increasing number of internet users.
- Online businesses: While online media and food delivery are reverting to pre-pandemic growth levels. travel and transportation will take some time to recover to pre-COVID levels as e-commerce continues to rise.
- Digital Payments: Offline-to-online behavior adjustments during the pandemic helped digital financial services, which include payments, remittances, lending, investments, and insurance, have strong growth from 2021 to 2022.
- Internet Economy: Predicted to reach $330 billion, the internet company in SEA expects to reach this number if investors focus on profitability.
But what does it look like to live in Singapore, the leading digital nation in SEA?
Connectivity is not a problem even in remote places with free Wireless@SG internet. Internationally-recognized credit cards are available to use at almost any shop in the city. Cafes and restaurants have available wifis and some places offer devices when you buy an item.
Singapore has flexible working arrangements. Co-working spaces are popular with workers who do not want to work in an office or at home.
Traffic is also not an issue with ride-hailing services and taxis available day to night. For Singapore’s Mass Transit System (MRT), you can buy a Smart Tourist Pass for unlimited travel or a Smartcard to top up any amount.
Buses run on a schedule where you can pay with a Smart Tourist Pass or the exact amount of cash since they do not give back the change.
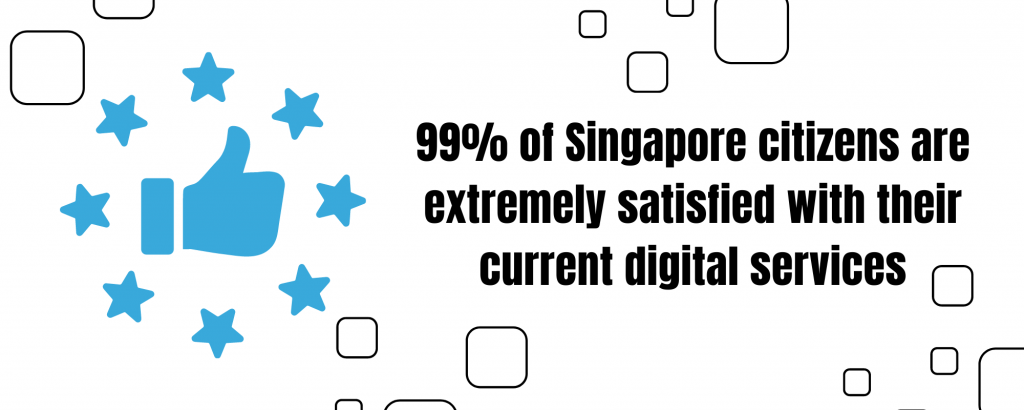
The digital government of Singapore has been running since 2015. The digital identity of the citizens is protected with quality cybersecurity. 99% of Singapore citizens are extremely satisfied with their current digital services.
The cost of living is higher but a survey in 2018 says ex-pats believe that Singapore is the best place to live especially for digital nomads who value internet connectivity.
Let’s remember Singapore is a small country by geographical size, and population of 5.45 million – it’s easier to become a highly integrated digital economy. Compare this against its neighboring SEA countries – Philippines (111 million), Vietnam (98.1 million), and Thailand (69.9 million).
Achieving a digital-first world
Digitalization can help underdeveloped nations to reduce friction between business and government. Singapore started its digitalization journey in the 1980s, currently, 95% of transactions in the country are digitized.
Today, there are 30% of digital natives around the world. But to fully adapt and take advantage of digital, there are some needed improvements.
Improvements in Digital Literacy: Cultivate digital literacy in every sector. Every affected member of digital transformation should be able to navigate the tools and applications used. They should also have the knowledge to use digital for personal purposes and convenience.
Because of the digital divide, some parts of the world still have some difficulties in using digital tools or are behind their urban counterparts. Improving digital literacy in these areas can also increase their chance of progress.
Educating Data Literacy: As the key to unlocking digital transformation, extracting value from data is necessary. Citizens should be able to:
- Create, manage, store, and maintain data.
- Report and analyze data for insights and recommendations.
- Access data needed in digital transformation.
Flexibility and Adaptability: The pillars of a digital nation must be open to change and should adapt to new conditions in the digital economy. Here are some of the qualities people need to have to adapt to digital transformation:
- Possess an open mind to new concepts, other people’s experiences, perspectives, and other cultures and values.
- Eager to learn new things constantly.
- Tenacity in facing adversity.
As one of the pillars, businesses also help in achieving a digital-first world. To create a high-performing digital enterprise that fully incorporates data and technology in all operations, McKinsey & Company suggests these six building blocks:
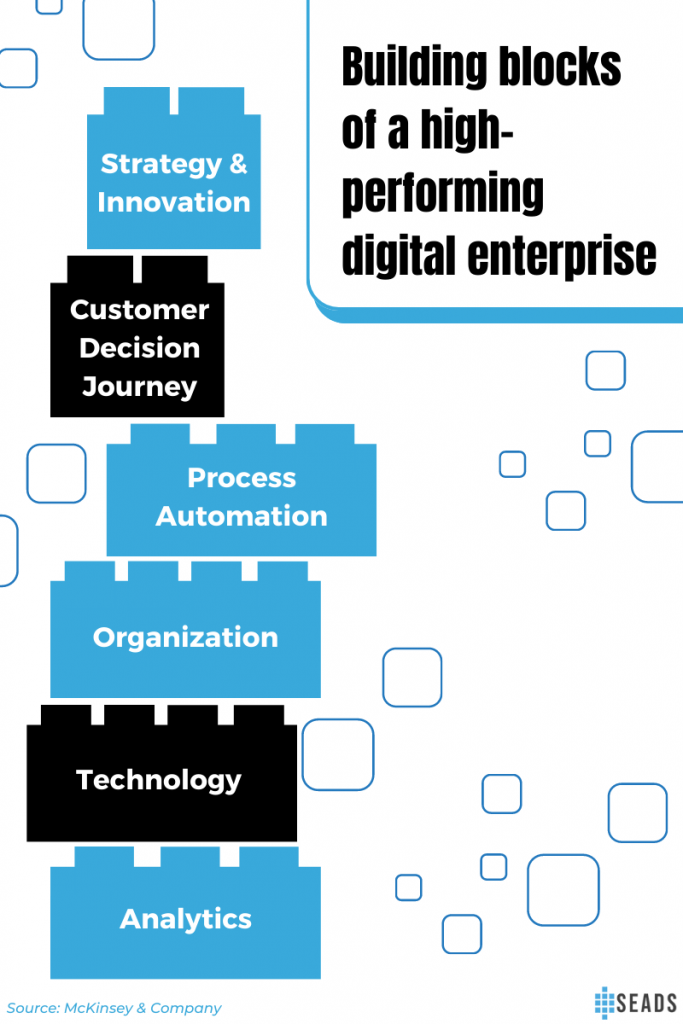
1. Strategy and innovation: Prioritize future value with data-driven insights. Assess what, where, when, and how a business value will be disrupted in the next five years.
2. Customer decision journey: Use data to precisely reach a quality audience. By personalizing the customer journey and understanding customer decisions, a business can make adjustments to its product, service, and delivery.
3. Process automation: Making processes instant and convenient is beneficial for overall business efficiency.
4. Organization: Strategize business operations. Outsourcing a part of a business for expertise, time, and focus can help the business run smoothly.
5. Technology: Acquire technology necessary for the business as IT transforms constantly and new resources are more advanced than others.
6. Analytics: Customer and competitor analysis collects necessary data for business goals and strategies.
The challenges to managing in a digital-first world
Digitalization is a long-term solution with a time-consuming process. Rewards and impacts are not noticeable without continuous efforts which can discourage businesses, governments, and consumers. But lagging is not an option especially when it affects sectors like education, tourism, employment, and more.
Below are the challenges in creating a digital-first world and how businesses, governments, and consumers manage them.
Misinformed and unclear digital strategy: The digital strategy needs to have a clear vision, defined goals, and attainable targets. It needs to have a roadmap to what it wants to achieve in every phase of the digital.
Financial constraints: The budget for digitalization includes planning, onboarding new tools, educating citizens, hiring specialists in digital and consultants, and more. Break down digital goals into smaller measurable phases by priority. Allocate resources and budget on the prioritized phases
Complexity and skill gaps: Tools and expertise are important in identifying and analyzing the data. Different tools have different usage, and the pillars of a digital nation need centralized data management tools. Ensure technology experience through digital training and education
Cybersecurity: Threats in data can disrupt digital transformation. The trust of the citizens is also affected when their security is at risk. Prepare for periodic risk assessments with security response plans to assure that any threats can be managed.
Developing nations in SEA embrace digital change for economic growth. Because a digital-first world is future-proof with long-term sustainable digital solutions. It entices investors and creates a digital economy convenient to every citizen.